Water inaccessibility places significant constraints on agriculture, impacting global food security and leading to increased human conflict due to scarcity in resources, Al-Ibrahim emphasized. He highlighted the critical need for sustainable water management practices to ensure both current and future generations can access clean water.
The minister's comments align with global concerns over water scarcity, as climate change and population growth exacerbate the situation. The United Nations estimates that by 2050, nearly 5 billion people could be facing water shortages. This prediction underscores the urgency of addressing water access issues to prevent severe humanitarian crises.
At the G20 session, Al-Ibrahim called for collaborative international efforts to improve water infrastructure and management. He stressed the importance of investing in technologies that can enhance water use efficiency and reduce wastage. By adopting innovative solutions, countries can mitigate the risks associated with water scarcity and promote sustainable development.
In Rio de Janeiro, discussions also focused on the economic impacts of water inaccessibility. Poor water management not only affects agriculture but also has far-reaching effects on health, education, and economic productivity. Access to clean water and sanitation is fundamental to reducing poverty and achieving sustainable development goals, Al-Ibrahim noted.
The minister's remarks were echoed by other international leaders who underscored the interconnected nature of water, food, and energy security. They pointed out that integrated approaches are necessary to tackle these challenges effectively. Coordinated policies that consider the nexus between water, food, and energy can lead to more resilient and sustainable systems.
The G20 meeting also highlighted successful case studies from various countries that have implemented effective water management strategies. These examples serve as valuable lessons for nations struggling with water scarcity. By learning from these initiatives, countries can develop tailored solutions that address their specific needs and circumstances.
Al-Ibrahim's call for action comes at a time when the world is grappling with the effects of climate change. Extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, are becoming more frequent and severe, further straining water resources. This reality necessitates a proactive approach to water management that includes both mitigation and adaptation strategies.
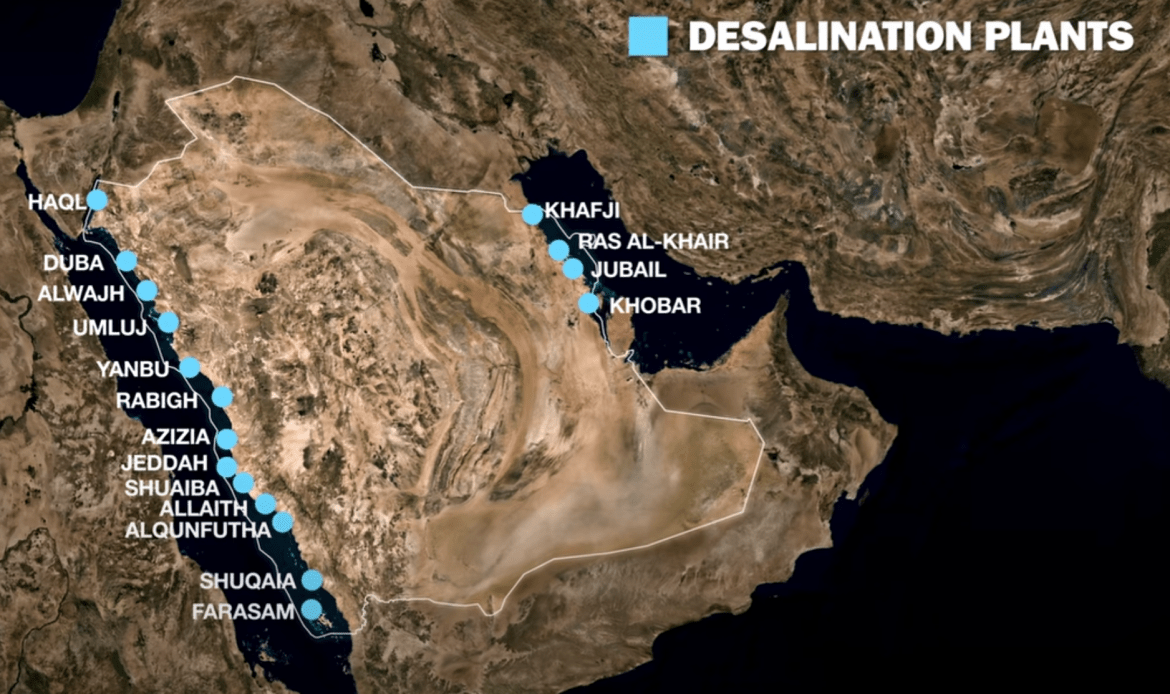
Innovations in water technology were a focal point of the discussions. Leaders discussed advancements such as desalination, wastewater recycling, and smart irrigation systems that can significantly enhance water availability and quality. These technologies offer promising solutions, but their implementation requires substantial investment and political will.
Topics
Gcc
